
SECTOR: Renewable Energies.
PROJECT: Development of advanced solutions for modular design and efficient management of high-capacity renewable hydrogen production plants.
ACHIEVEMENT: Research into new advanced technological solutions that enable modular design and efficient and safe management of future high-capacity hydrogen production plants, as well as the digitalization of the proposed solutions.
 The HYNNOVA project, coordinated by BOSLAN, part of Accenture, and with the participation of 11 other leading Basque companies in the hydrogen value chain, aims to create new technological solutions for production, storage, and compression that enable modular design and efficient and safe management of future hydrogen production plants.
The HYNNOVA project, coordinated by BOSLAN, part of Accenture, and with the participation of 11 other leading Basque companies in the hydrogen value chain, aims to create new technological solutions for production, storage, and compression that enable modular design and efficient and safe management of future hydrogen production plants.
In its effort to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, the European Union has endorsed renewable hydrogen as one of the main long-term energy vectors due to its advantageous characteristics. The production and consumption of renewable hydrogen are climate-neutral, have the capacity to triple the introduction of renewable energies within the energy system, and solve the problem of seasonal energy storage, enabling better management. Moreover, renewable hydrogen is positioned as a good alternative for the decarbonization of key economic segments such as maritime transport, aviation, or high-temperature industries (steel, cement, ceramics, and chemicals, primarily).
The goals set by the EU in the European Hydrogen Strategy require large hydrogen production plants to achieve high-efficiency ratios to reduce the Levelized Cost of Hydrogen (LCOH) and achieve greater competitiveness. These plants will need to be highly modular, flexible in operation, and optimize all processes involved in hydrogen production.
Due to technological limitations, current electrolysis stacks with power levels above 5 MW do not have sufficient reliability to operate at an industrial scale. This situation necessitates the parallel integration of a large number of equipment and systems in high-power plants (there are already projects proposing up to 200 MW of electrolysis). The design, management, and control of these facilities are complex and increase the risk of failure, as well as higher energy and water consumption. Additionally, the difficulty and scientific-technological challenges associated with the phases of compression and storage of hydrogen at different pressures must be addressed.
The objective of the HYNNOVA project is to solve these technological challenges posed by high-capacity hydrogen production plants and investigate new advanced solutions for production, storage, and compression that enable modular design and efficient and safe management. The consortium will also work on the digitalization of the proposed solutions.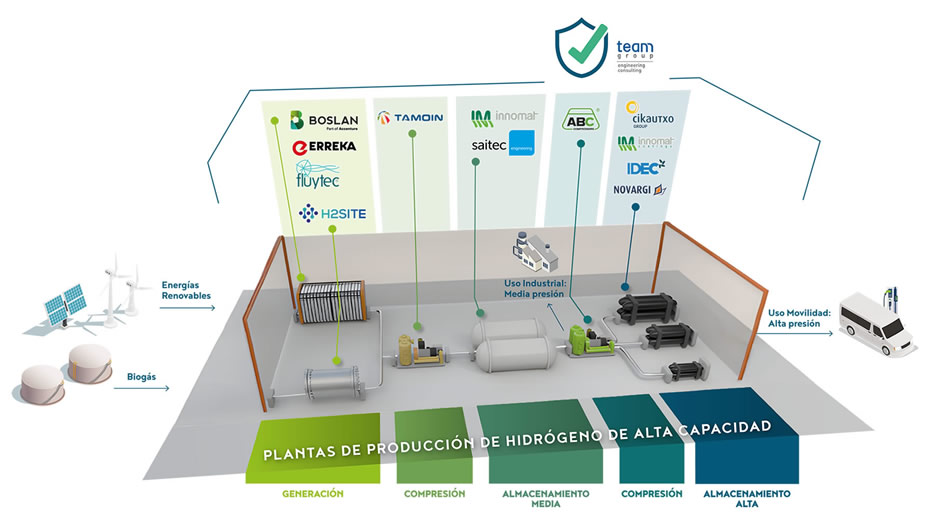 Project Hynnova Infographic.
Project Hynnova Infographic.
New solutions for green hydrogen generation
The engineering and consultancy firm BOSLAN, part of Accenture, leads the design of a process simulation model for an electrolyzer that will later be validated experimentally. The experimental campaign on two alkaline stacks of approximately 20 kW will also allow the quantification of parameters in semi-empirical equations and the optimization of operational and control strategies. The results obtained will enable better prediction of the electrolyzer’s behavior.
ERREKA will work on the design and development of smart fastenings for sealing the joints of the stacks, meeting safety requirements that exceed current standards, based on non-linear double-wave ultrasonic technology. This new solution will offer better control over the tightening of the stacks and their monitoring.
FLUYTEC, for its part, will design the electrodesionization (EDI) prototype for water purification in the recirculation circuit of the electrolyzer’s anode. The device will be tested on a 1 kW PEM test bench to validate the design and optimize the operation, control, and maintenance strategy of the prototype.
The start-up H2SITE will modify and characterize a new system capable of producing 20 Nm3/h of H2 and separating it at purity levels of 99% from a biogas stream. The new design seeks to optimize the performance and efficiency of the current system, as well as to operate continuously for over 1,000 hours.
New solutions for hydrogen compression
The research line led by TAMOIN will investigate hydrogen compression using metal hydrides. After characterizing different alloys that meet the system’s requirements, a thermodynamic analysis of the most promising alloy will be carried out to develop a simulation model for integrating residual heat from the electrolyzer and mechanical compressors. Next, a laboratory prototype will be designed and manufactured to emulate the metal hydride compressor and will be experimentally characterized to enable theoretical extrapolation of the results to an industrial scale.
ABC COMPRESSORS will conceive a mechanical compressor sizing tool aimed at achieving integral optimization that considers factors such as OPEX, CAPEX, efficiency, and safety across all aspects of the system.
New solutions for hydrogen storage
To develop solutions for low-pressure hydrogen storage, SAITEC will analyze different international standards in force and construction techniques using steel and concrete to determine their capabilities and limitations. This information will serve as a starting point for creating an optimized basic design of a mixed steel-concrete tank for large-scale stationary hydrogen storage at 250 bar. Structural and operational monitoring plans will also be developed to ensure the proper functioning of these tanks.
For high-pressure storage, the project aims to develop a rotomolded APA6 polymer liner (to be carried out by CIKAUTXO) and an injectable reinforced polymer liner (by INNOMAT) for type IV hydrogen tanks. The technology must be scalable, ensure low permeability to hydrogen, and offer a competitive material/process solution in terms of manufacturing costs.
INNOMAT will develop and characterize two types of anti-permeation barrier coatings for mixed steel-concrete tanks: a coating with good adhesion to steel, developed by the partner, and a hybrid organic-inorganic coating via sol-gel. In addition, different compositions of inorganic and hybrid organic-inorganic coatings will be studied and characterized, which will be applied to composites.
Finally, leveraging advanced composite material knowledge, the aim is to design, manufacture, and characterize a type IV demonstrator tank. IDEC will work on developing the fiber deposition/tape-laying process, while NOVARGI will focus on the tank and the overall storage system.
Modular solution for high-capacity renewable hydrogen production
As part of the project, BOSLAN, part of Accenture, will be responsible for developing a model of a high-capacity green hydrogen generation, storage, and compression plant for estimating investment and operating costs, with the goal of using this model to size new hydrogen plants. To do this, it will create individual models for the electrolyzer, the purifier, the MEGC or tube trailer, the compressor, cascade storage, and the regulation station for hydrogen pipeline supply. Other systems comprising the plant’s BoP (water treatment, cooling, N2 inertization system, etc.) will also be modeled. The connection of these modules will form the hydrogen plant scheme, which will include a graphical interface.
Advanced safety strategies in hydrogen infrastructures
TEAM will address risk evaluation in hydrogen infrastructures and develop safety protocols applicable to the efficient and safe management of high-capacity renewable hydrogen production plants by integrating fluid-dynamic numerical algorithms into traditional quantitative risk assessment analyses. Within the project, 3D numerical models of diffusion and flammability processes and “Robust Dynamic Based” algorithms will be developed, facilitating risk evaluation and the creation of corrective applications.
 Meeting of the members of the Hynnova consortium at the kickoff on September 23rd.
Meeting of the members of the Hynnova consortium at the kickoff on September 23rd.
HYNNOVA is a multi-year (2024-2026) industrial research collaboration project of strategic significance. The following entities are participating in the project: BOSLAN, part of Accenture (coordinator), ABC COMPRESORES, CIKAUTXO, ERREKA, FLUYTEC, H2SITE, IDEC, INNOMAT, NOVARGI, SAITEC, TAMOIN, and TEAM INGENIERÍA. Additionally, the project counts on the support of ABCTECH, CIKATEK, CLUSTER DE ENERGÍA, LEARTIBAI, and TECNALIA as agents of the Basque Network of Science, Technology, and Innovation (RVCTI), with BANTEC as the supporting consultancy. This project is funded by the Basque Government’s Department of Industry, Energy Transition, and Sustainability (HAZITEK Program) and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).
Interested entities can find more information on @HYNNOVA Project or on the project website www.hynnovaproject.com.
















